The final one Annual report on information security attitudes and behaviorsprinted by the Australian Cyber Collaboration Center in Australia, revealed that each Australian and world workforces are exhibiting numerous cybersecurity behaviors, together with a major tendency to share firm knowledge with synthetic intelligence instruments.
Interviewing 6,500 folks of various ages in eight international locations, together with Australia and New Zealand, the report discovered that IT and cybersecurity leaders are making progress towards enhancing safety with cybersecurity coaching. However, they’re nonetheless battling a lot of poor cybersecurity attitudes and behaviors of their workforce.
Cybersecurity is irritating for a lot of people and staff
The report discovered that Australians, like others all over the world, are more and more pissed off by the necessity for fixed on-line cybersecurity measures. In an Australian cybersecurity atmosphere that has included pervasive digitalisation of companies and providers, in addition to massive numbers of information breaches:
- 52% of respondents reported that on-line safety is “irritating” for them, whereas 44% admit to feeling intimidated by the complexities of on-line safety.
- There has been a major decline within the perceived worth of on-line safety, with solely 60% of Australians believing it’s price it, a drop of 9% from final 12 months.
- Generation Z and Millennials are probably the most pessimistic about their capacity to remain secure on-line, and lots of have scaled again their on-line actions as a consequence of these issues.
The findings counsel rising discontent with the damaging features of the digital atmosphere wherein folks work. The complexities and frictions of managing cybersecurity to reduce dangers may trigger disengagement from safety practices, which may pose a menace to employers’ knowledge safety measures.
SEE: APAC staff select comfort and pace over cybersecurity
Individuals are outsourcing the accountability of cybersecurity
Individuals more and more count on others to be chargeable for the safety of their data, together with the expertise business and expertise platforms. In Australia, 90% of individuals throughout all age teams imagine apps and platforms must be chargeable for defending their private data. Furthermore:
- IT and safety departments are thought of most chargeable for safeguarding data within the office, though an increasing number of staff at the moment are inserting extra accountability on the expertise sector.
- The share of people that take into account themselves primarily chargeable for security fell by 7% in comparison with 2023, bringing the overall to 59%. Personal accountability within the office amounted to solely 36%.
- The Australian Cyber Collaboration Center discovered “widespread complacency”, with 43% believing their units are mechanically safe. That share was larger for youthful generations.
Premium: How to Create a Cybersecurity Awareness Program
“Complacency and frustration are harmful mixtures within the struggle towards cybercrime in Australia,” Matthew Salier, chief government of the Australian Cyber Collaboration Centre, stated in an announcement. “Vulnerability to cyber assaults is particularly regarding amongst youthful generations as a result of they do not take ample precautions, rely an excessive amount of on others, or assume that their units are safe.”
The foremost behaviors associated to cybersecurity nonetheless have room for enchancment
The report discovered that folks proceed to stumble over cybersecurity hygiene, which may affect employers:
Password utilization: The use of non-public data for passwords, similar to relations or pet names, has elevated throughout all generations, with Gen Z the most definitely group to make use of these passwords (52%). Organizations ought to notice that the popular technique of managing passwords amongst these with multiple on-line account is to write down them down in a bodily pocket book (29%), whereas solely 12% use a password supervisor.
Multi-factor authentication: As many as 81% of respondents have heard of MFA, up 11% from final 12 months, which is meant to assist cybersecurity professionals implement the expertise. However, adoption is inconsistent. The report discovered that the adoption of MMA may very well be irritating for the person expertise, with many youthful customers who’ve tried to implement MFA up to now on their units, having deserted it.
Phishing detection: Survey individuals had been general prepared to acknowledge phishing emails or malicious hyperlinks, with 67% throughout all geographies saying they felt assured they might achieve this. However, 10% of respondents stated they had been uncertain; The report’s evaluation suggests that is because of the rising sophistication of phishing makes an attempt, together with criminals utilizing synthetic intelligence.
AI instruments must be a priority for cyber and knowledge professionals
AI instruments are creating new cybersecurity and knowledge safety issues within the office:
- In Australia, greater than half of employed individuals (52%) have but to obtain any coaching within the secure use of AI, regardless of issues similar to knowledge leaks and over-reliance on responses.
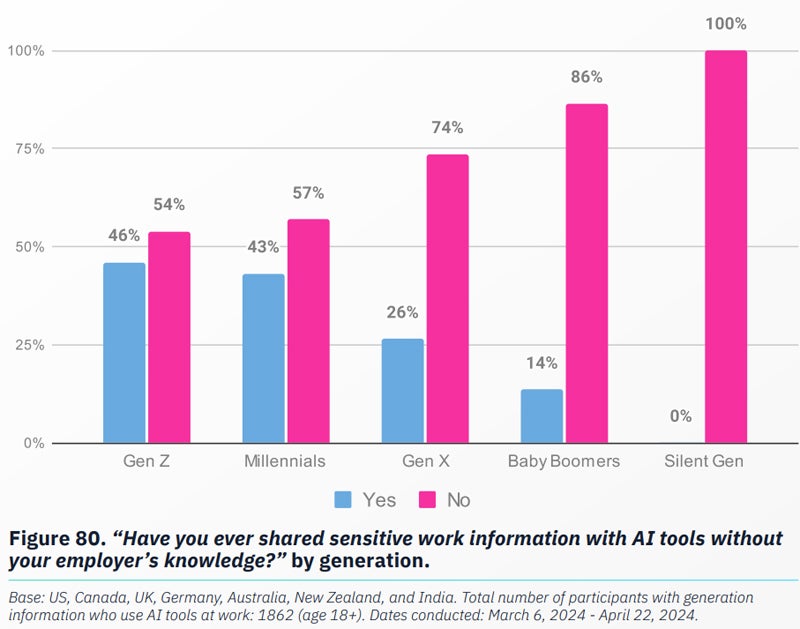
- A surprising 38% of world respondents throughout all jurisdictions surveyed admitted to sharing delicate work data with AI with out their employer’s information.
- The prevalence of staff sharing knowledge with AI was larger amongst youthful generations, with 46% of Generation Z and 43% of Millennials sharing knowledge with AI, in comparison with 26% of Generation X .
Organizations not trusted to implement AI responsibly
There is proof that people might have low confidence within the capacity of organizations and IT to implement AI:
- Confidence in firms implementing AI responsibly was lowest in Australia, the place solely 35% believed firms had been as much as the problem of implementing AI ethically.
- Millennials in Australia worry synthetic intelligence will make rip-off detection much more tough.
Academy: Improve your skills with our Cyber Security Expert Training Package 2024
There are some world issues that AI will affect employment. Nearly half of Generation Z (48%) and Millennials (49%) imagine AI is prone to trigger modifications to their employment standing, though Baby Boomers and the Silent Generation had been much less involved about AI’s affect on their work (13% and 49%) 11%, respectively).
Cybersecurity coaching gives a silver lining for IT professionals
While the report reveals some cybersecurity behaviors, IT and cybersecurity professionals got indications that the cybersecurity coaching applications they’ve carried out seem to extend cybersecurity consciousness amongst their staff:
- The majority (83%) of respondents who accessed coaching within the office or place of training discovered it helpful.
- The largest impacts reported had been on recognizing and reporting phishing messages (52%) and utilizing MFA (45%).
- Overall, the report discovered a rise within the perceived affect of coaching on all security behaviors in comparison with 2023.
“As the menace panorama evolves with the introduction of synthetic intelligence,” Salier concluded, “we should present people and organizations in Australia with the instruments they should navigate this advanced atmosphere.”






