The Office of the Australian Information Commissioner’s newest report on notifiable knowledge breaches has revealed a speedy improve in notifiable knowledge breaches nationwide within the first six months of 2024, a 9% improve in comparison with the final six months of 2023 and the best variety of notifications since 2020.
The report, released in Septemberconfirmed that current knowledge breaches, together with the MediSecure prescription service breach that affected 12.9 million Australians, have prompted a robust response from the OAIC. The company has warned it’s taking a harder stance on knowledge privateness and breaches, stressing that organisations should prioritise privateness of their knowledge practices.
Which industries have suffered essentially the most knowledge breaches?
The OAIC has been publishing statistical data on knowledge breach notifications because the launch of the Notifiable Data Breaches program in Australia in 2018. The newest report revealed:
- A complete of 527 notifications had been obtained from January to June 2024, a rise of 9% in comparison with the 485 notifications obtained from July to December 2023.
- The final six months have seen the best variety of notifications obtained since July to December 2020, within the midst of the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic.
- The high 5 industries experiencing knowledge breaches had been healthcare suppliers (102 breaches), the Australian Government (63), finance (58), schooling (44) and retail (29).
- Malicious or felony assaults, each exterior and inside, had been the supply of 67% of all knowledge breaches, adopted by human error (30%) and system failures (3%).
- Malicious or felony assaults included cyber incidents (57%), social engineering/impersonation (27%), theft of paperwork or knowledge archives (8%), and threats from unauthorized staff/insiders (8%).
- Most of the reported breaches (63%) concerned 100 individuals or fewer, however there have been eight large-scale breaches that impacted greater than 100,000 individuals, together with the “largest MediSecure breach” in Australia.
SEE: Australian organisations are seeing the best fee of knowledge breaches
Cyber incidents dominate malicious and felony assaults in Australia
Cyber incidents proceed to be a prevalent trigger of knowledge breaches, accounting for 38% of all breaches. Cyber incidents had been outlined as these involving phishing, ransomware, compromised or stolen credentials (methodology unknown), brute-force assaults, hacking, and malware, however not social engineering-style assaults.
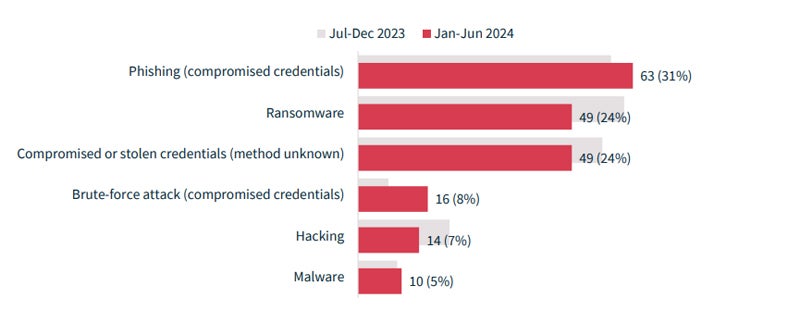
Among the assorted malicious or felony assaults, cyber incidents had the best influence on people. On common, 107,123 people had been affected by the 201 cyber incidents, whereas a mean of 4,709 people had been affected by incidents brought on by dishonest staff or insider threats.
In the report, Australian Privacy Commissioner Carly Kind stated the continued prevalence of cyber incidents in knowledge breach totals reported to the OAIC occurred “as our rising reliance on digital instruments and on-line providers exposes our knowledge extra ceaselessly to malicious cyber attackers.”
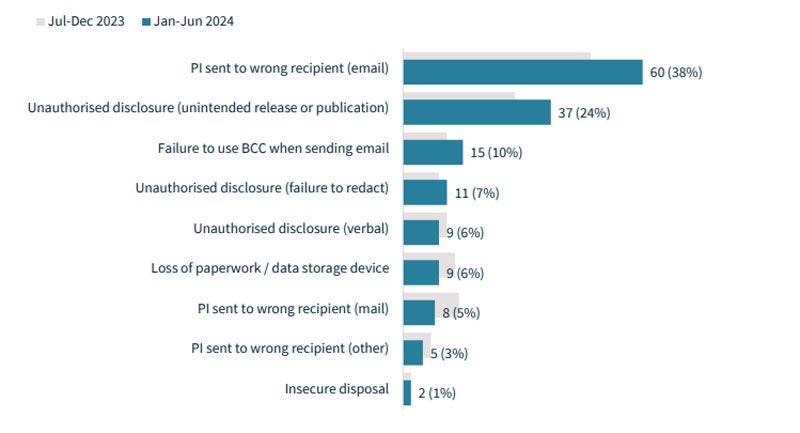
However, human error nonetheless accounts for 30% of reportable knowledge breaches. The high human error classes had been:
- Personally identifiable data despatched to the incorrect e mail recipient (38%).
- Unauthorized disclosure of knowledge or inadvertent dissemination or publication (24%).
- Failure to make use of the BCC (blind carbon copy) possibility when sending emails (10%).
Spike in knowledge breaches places Australian authorities businesses within the highlight
The OAIC famous that the Australian authorities reported the second highest variety of knowledge breaches of all sectors, its highest rating ever, though it had beforehand been among the many high 5 breached sectors. According to the report:
- Government businesses reported 63 knowledge breaches from January to June 2024, accounting for 12% of all knowledge breach notifications in Australia.
- The authorities accounted for the biggest variety of social engineering or impersonation knowledge breaches, making up 42 % of such incidents. According to the OAIC, these breaches sometimes concerned a risk actor impersonating a buyer to achieve entry to an account utilizing official credentials.
- The authorities was additionally slower to behave: it obtained the best proportion (87%) of notifications the place the company recognized the incident greater than 30 days after it occurred, whereas 78% of presidency notifications had been made greater than 30 days after the company grew to become conscious of the incident.
SEE: Is the Australian public sector prepared for a significant cybersecurity incident?
How can organizations cease knowledge breaches?
Security consultants regularly remind organizations that many knowledge breaches or cyber assaults could possibly be prevented by implementing fundamental cybersecurity measures. The OAIC has made a number of suggestions primarily based on traits in knowledge breach knowledge.
Mitigating Cyber Threats
The OAIC beneficial implementing multifactor authentication as a primary precedence to cease cyber threats, or sturdy password administration insurance policies and practices if MFA shouldn’t be accessible. The company additionally beneficial:
- Implement multi-layered safety controls to keep away from a single level of failure.
- Define ranges of entry to data primarily based on roles and duties.
- Leverage safety monitoring to detect, reply to, and report incidents or uncommon exercise.
The OAIC has indicated frameworks that embrace The Eight Essentials of Australiathe Australian Directorate of Signals Information Security Manualthe National Institute of Standards and Technology primarily based within the United States Cyber Security Frameworkin addition to the International Organization for Standardization’s data safety administration requirements ISO 27001 and ISO 27002, as measures to information improved practices.
Extended provide chain dangers
According to the OAIC, some large-scale knowledge breaches are brought on by provide chain compromises, such because the breach that affected MediSecure and one other Accident involving OutaboxThe company added that outsourcing the administration of non-public data to 3rd events stays a prevalent danger.
The company stated corporations ought to think about the dangers of outsourcing private data administration early within the procurement course of, together with to cloud suppliers. It additionally beneficial that organizations put in place a strong vendor danger administration framework, together with stronger safety measures.
Addressing the human issue
The OAIC famous that people stay a big risk to sturdy privateness practices. These threats embrace breaches resulting from human error or staff fooled by phishing.
The company urged organizations to implement technical measures to scale back errors and pressured that coaching workers is crucial to make sure they perceive their privateness and safety obligations. It additionally beneficial prioritizing workers coaching in safe data administration practices.
Incorrect configuration of knowledge saved within the cloud
Some organizations are “neglecting” cloud safety as they digitally remodel, the OAIC stated. Several knowledge breaches throughout the quarter occurred when an Australian entity misconfigured safety settings resulting from human error, leaving private data weak to unauthorized entry or public disclosure.
The OAIC stated organizations shouldn’t assume that the accountability for cloud safety falls on the supplier. The company pressured that cloud safety and administration must be a precedence, highlighting the significance of measures corresponding to safe entry controls through MFA, IP entry controls, and encryption.






